Table of Contents
In Thailand, where sexually transmitted infections (STIs) like gonorrhea, HIV and Chlamydia are prevalent, it’s essential to understand the process of testing for gonorrhea, especially in individuals who may have co-infections. Gonorrhea, an infection caused by the bacterium Neisseria gonorrhoeae, can complicate the course of HIV or Chlamydia. Early detection and treatment are key to reducing the risks associated with these co-infections. This step-by-step guide explains how to test for gonorrhea in people with HIV or Chlamydia in Thailand using various diagnostic tools, including Gonorrhea Test Kits and Gonorrhea Rapid Test Kits.
Step 1: Why Testing for Gonorrhea in Co-Infected Individuals is Crucial?
Individuals living with co-infections, such as HIV and Chlamydia, face increased health risks when contracting additional STIs like gonorrhea. Testing for gonorrhea in these individuals is vital because:
- HIV Increases Susceptibility: HIV weakens the immune system, making it harder for the body to fight infections. If someone with HIV acquires gonorrhea, it may lead to more severe health complications, including increased viral load and a higher likelihood of transmitting HIV to others.
- Chlamydia and Gonorrhea Often Co-Exist: Both gonorrhea and Chlamydia can infect the same anatomical sites, such as the cervix, urethra or rectum, making simultaneous testing essential for accurate diagnosis and treatment.
- Risk of Reinfection: Co-infected individuals may be more vulnerable to reinfection, especially if gonorrhea is left untreated. This can result in persistent or recurrent symptoms and more complex health challenges.
It’s crucial to regularly test for gonorrhea and monitor for co-infections in individuals who are already infected with HIV or Chlamydia. Early intervention can prevent further complications and reduce the risk of transmission.
Step 2: Common Symptoms of Gonorrhea in Co-Infected Individuals
Recognizing the symptoms of gonorrhea can aid in timely testing. While many individuals may not show any symptoms, co-infected individuals may experience more noticeable signs. Common symptoms of gonorrhea include:
- Painful Urination: A burning sensation during urination is one of the most common symptoms of gonorrhea.
- Abnormal Discharge: A thick, yellow or green discharge from the genital tract is a common sign of gonorrhea in both men and women.
- Pelvic Pain: Women with gonorrhea may experience pelvic pain or discomfort, especially during sexual intercourse.
- Rectal Symptoms: Individuals who engage in receptive anal sex may experience pain, itching or discharge from the rectum.
- Sore Throat: Throat gonorrhea, though less common, can cause symptoms like a sore throat, difficulty swallowing and swollen lymph nodes.
Many people with gonorrhea are asymptomatic, especially in the early stages of infection. This is why Gonorrhea Screening Tests and regular STI check-ups are necessary, particularly for individuals with co-infections like HIV or Chlamydia.

Step 3: How to Test for Gonorrhea in Co-Infected Individuals?
Testing for gonorrhea in people with co-infections requires careful attention to detail, as simultaneous infections can sometimes complicate diagnosis. Here’s a step-by-step guide to testing for gonorrhea, including both clinical and home-based options.
Step 3.1: When to Test for Gonorrhea
It’s important to test for gonorrhea at regular intervals, particularly for individuals who are already living with HIV or Chlamydia. The general recommendation is to:
- Test Annually: If you are sexually active and living with HIV, you should test for gonorrhea at least once a year.
- Test During Each STI Screening: If you have Chlamydia, you should undergo gonorrhea testing during every STI screening to check for potential co-infection.
- Test After Unprotected Sex: If you have engaged in unprotected sex, particularly with new or multiple partners, it’s crucial to get tested for gonorrhea as soon as possible.
Step 3.2: At-Home Testing with a Gonorrhea Self Test Kit
For people in Thailand who may not have easy access to clinics or healthcare facilities, Gonorrhea Self-Test Kits offer a convenient and private way to check for gonorrhea. These kits can be used at home and they typically include everything needed to collect a sample.
- Collect the Sample
For a Gonorrhea Home Test Kit, you will typically collect a urine sample or use a swab provided in the kit to collect a sample from the infected area (e.g., cervix, urethra, throat or rectum). It’s important to follow the instructions carefully to ensure the sample is collected correctly. - Perform the Test
After collecting the sample, follow the instructions to add the sample to the test device. Many self-test kits will show a result within 10 to 20 minutes. A positive result may indicate the presence of gonorrhea and further medical consultation is recommended. - Read the Results
Results typically appear as a line or mark on a test strip. One line indicates a negative result, while two lines may indicate a positive result. In case of uncertainty, contact a healthcare professional to confirm the result.
Step 3.3: Clinical Testing at a Healthcare Facility in Thailand
For a more comprehensive and reliable diagnosis, individuals can visit healthcare facilities in Thailand. A doctor or healthcare provider will typically perform the following:
- Physical Examination
The healthcare provider will ask about symptoms and sexual history. They may also perform a physical examination to check for signs of gonorrhea, such as discharge or inflammation in the genital, rectal or throat areas. - Sample Collection
A swab will be taken from the potentially infected area (e.g., urethra, cervix, throat or rectum). This sample will be sent to a laboratory for testing. Alternatively, urine tests can also be used in some cases. - Laboratory Analysis
Once the sample is collected, it is sent to a laboratory for analysis, where technicians will test it for the presence of Neisseria gonorrhoeae, the bacteria that cause gonorrhea. This process can take several days.
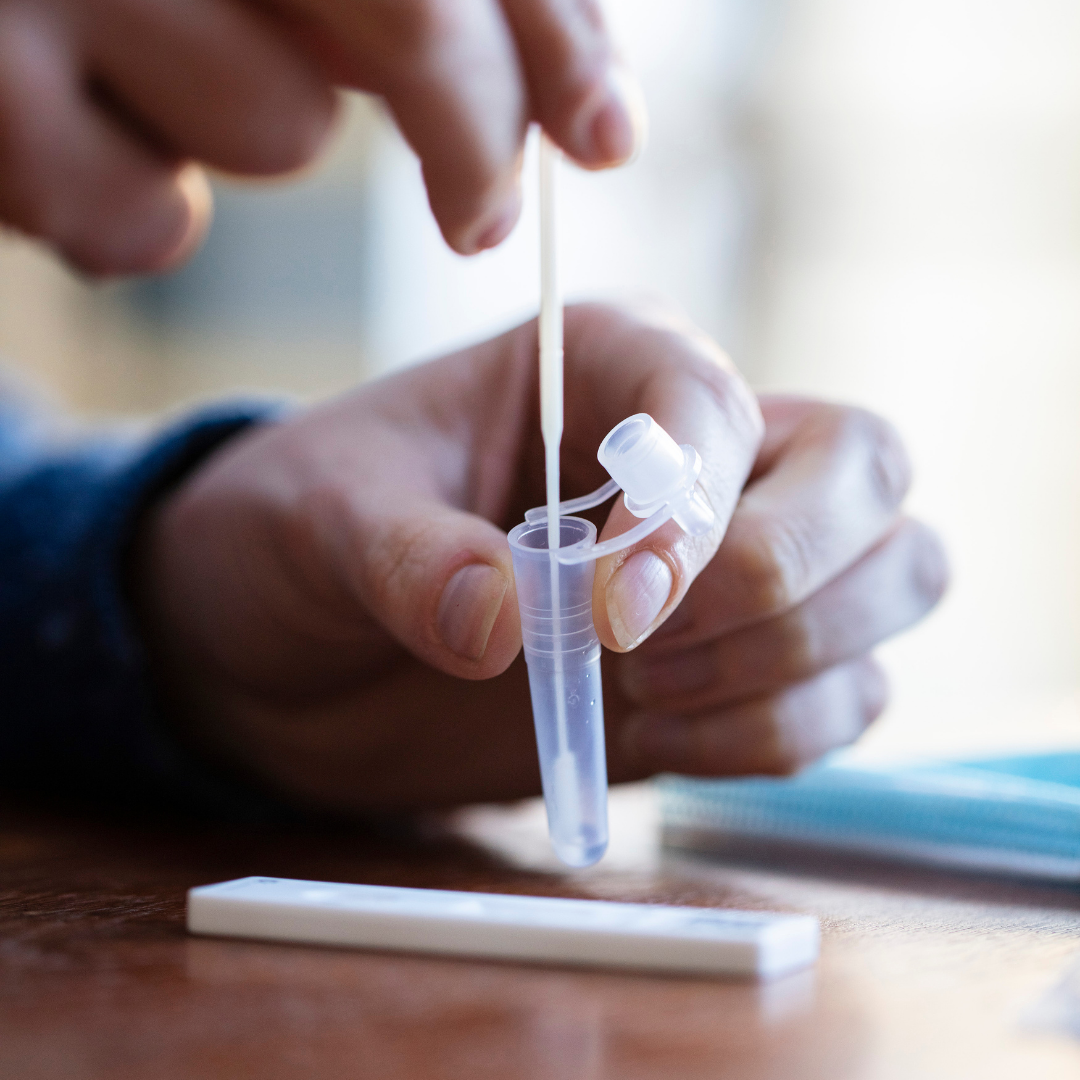
Once the results are in, a healthcare provider will contact you with the results. If gonorrhea is confirmed, a treatment plan, usually involving antibiotics, will be prescribed. It is essential to follow the entire treatment regimen, even if symptoms improve before completing the antibiotics.
Step 4: Treatment for Gonorrhea and Co-Infections in Thailand
If gonorrhea is diagnosed, it can be treated effectively with antibiotics. However, the presence of co-infections, like HIV or Chlamydia, may require additional considerations during treatment.
- Antibiotic Therapy: Gonorrhea is typically treated with a combination of antibiotics, such as ceftriaxone, to ensure that the infection is cleared. If you are co-infected with Chlamydia, you may receive additional antibiotics.
- Follow-Up Care: After treatment, it is important to follow up with your healthcare provider to ensure the infection has been completely eradicated. Some individuals may require additional rounds of testing, especially if they have HIV, which may make them more susceptible to reinfection.
Step 5: Preventing Gonorrhea and Co-Infections in Thailand
Preventing gonorrhea and other STIs is the best way to protect your health. Here are some key preventive measures:
- Use Protection: Consistently using condoms during sex is one of the most effective ways to prevent gonorrhea and other STIs.
- Regular Testing: Regular screenings, especially for individuals with HIV or Chlamydia, help detect infections early and reduce the risk of complications.
- Limit Sexual Partners: Reducing the number of sexual partners and being in a mutually monogamous relationship can help decrease the risk of gonorrhea and other STIs.
- Vaccination: Vaccines for certain STIs, such as HPV, can help reduce the risk of co-infections.

Conclusion
Testing for gonorrhea in individuals with co-infections like HIV or Chlamydia is crucial for managing sexual health, especially in Thailand, where STIs are prevalent. By recognizing the symptoms, using Jal Medical, as a leading gonorrhea diagnostics manufacturer and seeking timely medical care, individuals can detect gonorrhea early and begin treatment quickly. Regular testing, along with preventive measures, can significantly reduce the risk of complications and transmission of gonorrhea and other STIs.
FAQs
How often should I test for gonorrhea if I have HIV or Chlamydia?
It’s recommended to test for gonorrhea at least once a year if you are living with HIV or Chlamydia. If you engage in unprotected sex, more frequent testing may be necessary.
Can I test for gonorrhea at home?
Yes, Gonorrhea Home Test Kits are available and can be used to collect a sample and test for gonorrhea at home. Results are typically available within 10-20 minutes.
What are the treatment options for gonorrhea in Thailand?
Gonorrhea is typically treated with antibiotics, such as ceftriaxone. If you have Chlamydia, additional antibiotics like azithromycin may be prescribed.
How long does it take to get results from a gonorrhea test?
Results from Gonorrhea Rapid Test Kits are available within 10-20 minutes. Laboratory results may take a few days to process.

